Nebulizer vs. Inhaler: Understanding the 2-in-1 Advantage of TTLIFE Home Oxygen Concentrators
Home oxygen concentrators are becoming increasingly popular for individuals seeking respiratory relief and improved oxygen levels in the comfort of their own homes. These devices, also known as oxygen generator for home, work by filtering out nitrogen from the surrounding air, leaving behind concentrated oxygen that is then delivered through nasal cannulas.
However, many people with respiratory conditions may also benefit from nebulized medication delivery. This is where understanding the difference between a nebulizer and an inhaler becomes crucial. Let's delve deeper and explore the benefits of home oxygen concentrators with a built-in nebulizer function, a key feature offered by TTLIFE.
Nebulizers vs. Inhalers: Understanding the Difference
Both nebulizers and inhalers are used to deliver medication directly to the lungs for respiratory conditions like asthma, COPD, and cystic fibrosis. However, they differ in their methods of delivery:
1. Nebulizers: Delivering Liquid Relief

Nebulizers are electric or battery-powered devices that convert liquid medication into a fine mist for inhalation through a mouthpiece or mask. This process allows the medication to reach the deep recesses of your lungs, making it particularly effective for treating:
- Acute respiratory illnesses: Nebulized medication can quickly deliver bronchodilators to open airways during asthma attacks or COPD exacerbations.
- Chronic respiratory conditions: Regularly scheduled nebulized medication can help manage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cystic fibrosis.
- Delivery to patients with limitations: Nebulizers are ideal for patients who have difficulty coordinating inhaler techniques, such as young children, elderly individuals, or those experiencing respiratory distress.
Types of Nebulizers:
- Jet nebulizers: These are the most common type, using compressed air to create the mist. They can be bulky and noisy, but are generally affordable.
- Ultrasonic nebulizers: These nebulizers use ultrasonic vibrations to generate the mist. They are quieter and more portable than jet nebulizers, but tend to be more expensive.
- Mesh nebulizers: The latest technology, mesh nebulizers are highly portable, quiet, and efficient. They use a vibrating mesh to create the mist and are ideal for on-the-go use.
Benefits of Nebulizers:
- Effective delivery of medication directly to the lungs
- Ideal for patients with difficulty using inhalers
- Can accommodate a broader range of medications
Drawbacks of Nebulizers:
- Bulky and less portable compared to inhalers
- Treatment sessions can take longer than using an inhaler
- Requires cleaning and maintenance after each use
- Can be noisy due to the compressor
2. Inhalers: A Precise Dose

Inhalers are compact, portable devices that deliver medication in a pressurized aerosol form. While convenient and easy to use, inhalers require proper coordination to ensure the medication reaches the lungs effectively.
Types of Inhalers:
- Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs): These inhalers use a propellant to deliver a precise amount of medication as an aerosol mist. Proper coordination is required to activate the inhaler and inhale the medication effectively.
- Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs): These inhalers rely on your inhalation force to activate the release of powdered medication. Proper inhalation technique is crucial for optimal medication delivery.
Benefits of Inhalers:
- Compact and portable for convenient use
- Treatment sessions are typically quicker than nebulizer treatments
- Some types (DPIs) do not require coordination with inhalation
Drawbacks of Inhalers:
- Requires proper technique for effective medication delivery
- May not be suitable for everyone, especially those with weak inhalation strength
- Limited range of medications compared to nebulizers
Choosing Between a Nebulizer vs Inhaler
Ultimately, the choice between a nebulizer and inhaler depends on your specific needs and doctor's recommendation. Here are some factors to consider:
- Your medical condition: Certain conditions, like COPD, might benefit from a combination of nebulized medication and inhaled bronchodilators.
- Severity of symptoms: During an acute asthma attack, a nebulizer might be preferred for faster medication delivery.
- Your ability to use an inhaler: Proper inhaler technique is crucial for effective medication delivery. If you have difficulty coordinating hand-to-mouth actions or breathing deeply, a nebulizer may be a better choice.
- Portability: If you need medication on-the-go, an inhaler might be more convenient than a nebulizer.
Nebulizers and inhalers are both valuable tools for delivering medication to the lungs. The best option for you depends on your specific medical condition, medication needs, and ability to use each device effectively.
Atomization: A Breath of Fresh Air for Respiratory Health
Atomization plays a crucial role in respiratory health by transforming liquid medication into a fine mist for efficient delivery directly to your lungs. Here's how it benefits those managing respiratory conditions:


- Enhanced Medication Delivery: Compared to pills or tablets, atomization breaks down medication into tiny particles, allowing for deeper penetration into the lungs. This ensures faster and more effective medication absorption.
- Relief for Various Conditions: Atomization therapy is widely used to treat respiratory illnesses like COPD, asthma, cystic fibrosis, and bronchitis. It can deliver medications like bronchodilators, mucolytics, and antibiotics directly to the airways, providing targeted relief for various symptoms.
- Improved Breathing: By delivering medication directly to the lungs, atomization therapy can help to loosen mucus congestion, open airways, and ease breathing difficulties. This leads to improved oxygen intake and a reduction in symptoms like shortness of breath and coughing.
- Effective for All Ages: Atomization therapy is a versatile treatment option suitable for people of all ages, from infants and children to adults and seniors.
Here are some common atomization devices used for respiratory health:
- Nebulizers: These are electric or battery-powered devices that convert liquid medication into a mist for inhalation.
- Mesh Nebulizers: A newer technology, mesh nebulizers offer a quieter and more portable option for atomization therapy.
The Advantage of a 2-in-1 Home Oxygen Concentrator with Nebulizer Function
TTLIFE's home oxygen concentrators series boasts a unique 2-in-1 functionality. This home oxygen concentrators not only provide a steady stream of concentrated oxygen but also integrate a nebulizer function. This offers several advantages:
- Convenience: Having both oxygen therapy and nebulization capabilities in one device eliminates the need for a separate nebulizer, simplifying your home respiratory care routine.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By combining these functionalities, you save money compared to purchasing separate units.
- Improved Medication Delivery: The nebulizer function in TTLIFE's home oxygen concentrators ensures efficient delivery of nebulized medication alongside the oxygen flow, maximizing its effectiveness.
Introducing the TTLIFE Home Oxygen Concentrator 105W
The TTLIFE Home Oxygen Concentrator 105W exemplifies the benefits of a 2-in-1 design. Here's a closer look at its key features:
- Integrated Atomization Function: The built-in nebulizer allows for efficient atomization of medication during oxygen therapy.
- High-Efficiency Oxygen Production: Backed by a German research and development team, this oxygen concentrator delivers a stable oxygen output with a concentration range of 30% to 90%.
- Adjustable Flow Rate: The oxygen flow rate is adjustable from 1 to 7 liters per minute, allowing you to personalize your therapy based on your doctor's recommendations.
- Quiet Operation: Engineered with a pure copper oil-free compressor, the oxygen concentrator operates at a noise level as low as ≤48dB(A), ensuring a peaceful environment during use.
- User-Friendly Controls: The IMD large color panel displays vital information clearly. Flow regulation, voice broadcast function, timer operation, and an infrared remote control provide convenient operation.
- Advanced Safety Features: TTLIFE prioritizes safety with features like automatic shut-off upon current overload or high working temperature.
Nebulizers vs. Inhalers: Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How do I use a nebulizer?
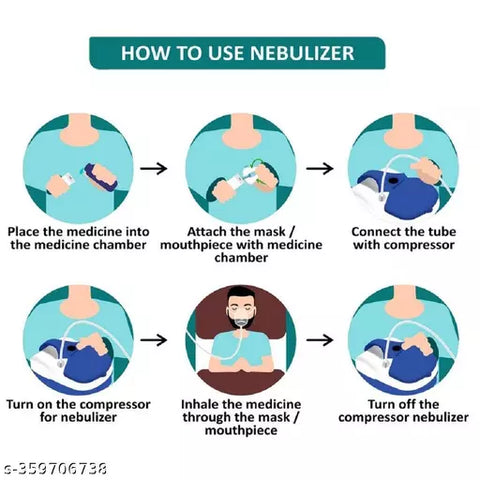
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Prepare the medication according to your doctor's instructions.
- Fill the nebulizer cup with the medication.
- Attach the mouthpiece or mask to the nebulizer.
- Turn on the nebulizer and breathe in slowly and deeply through the mouthpiece or mask.
- Continue for the prescribed amount of time or until all the medication is gone.
- Wash the nebulizer cup, mouthpiece or mask, and tubing with warm soapy water after each use.
Q. How do I use an inhaler?

- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Remove the cap from the inhaler.
- Shake the inhaler well (for MDIs).
- Breathe out slowly and completely.
- Place the mouthpiece between your lips and form a seal.
- Press down on the canister or inhale as you press down (depending on the type of inhaler).
- Hold your breath for a few seconds, then breathe out slowly.
- Repeat steps 4-7 for the prescribed number of puffs.
- Rinse your mouth with water after using the inhaler (for MDIs).
- Replace the cap on the inhaler.
Q. How often should I clean my nebulizer and inhaler?
- Nebulizer: Clean the cup, mouthpiece or mask, and tubing after each use. Disinfect them according to the manufacturer's instructions at least once a week.
- Inhaler: Most inhalers don't require cleaning. However, you should wipe the mouthpiece with a clean, dry cloth once a week.
Q. What kind of medication can be used in a nebulizer?
Nebulizers can deliver a wider variety of medications compared to inhalers. However, it's crucial to only use medication prescribed by your doctor and specifically formulated for nebulization. Here are some common types of medications used in nebulizers:
- Bronchodilators: These medications relax the muscles in your airways, making it easier to breathe. Examples include albuterol, levalbuterol, and salmeterol.
- Mucolytics: These medications help thin and loosen mucus in your airways, making it easier to cough up. Examples include acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) and dornase alfa (Pulmozyme).
- Antibiotics: Inhaled antibiotics may be used to treat respiratory infections caused by bacteria.
- Anti-inflammatory medications (corticosteroids): These medications can help reduce inflammation in the airways, which is beneficial for conditions like asthma. However, it's important to note that corticosteroids are not typically the first line of treatment for nebulized medications.
Breathe Easy with TTLIFE Home Oxygen Concentrators
At TTLIFE, we understand the importance of effective respiratory care solutions. Our innovative 2-in-1 home series oxygen concentrators offer the combined benefits of oxygen therapy and nebulization. This allows you to receive supplemental oxygen while simultaneously delivering nebulized medication for targeted relief.
Browse TTLIFE's selection of oxygen generator for home today and discover how you can breathe easier at home and manage your respiratory health effectively!



